Menu



The Cordyceps fungus, also known as the "zombie fungus," is one of nature's most remarkable creations. Famous for its ability to infect and control the behavior of insects, Cordyceps offers a glimpse into the extraordinary complexities of the natural world.
Beyond its eerie life cycle, the fungus has made a name for itself in traditional medicine and modern supplements, celebrated for its purported health benefits.
Let’s explore how this fascinating organism operates, its role in ecosystems, and its growing use in the wellness industry.
Cordyceps is a genus of fungi comprising over 400 species [1], uniquely characterized by their parasitic ability to hijack the bodies of insects. These fungal species infiltrate their hosts—such as carpenter ants, caterpillars, or beetles—by attaching fungal spores to the insect’s exoskeleton and penetrating its body.
Once inside, this parasitic fungus commandeers the host’s central nervous system, eventually steering its behavior. In a remarkable feat of biological control, the infected insect is driven to climb to an elevated position, ideal for spore dispersal when the fungus later emerges.
This chilling survival strategy has made Cordyceps a subject of both scientific fascination and ecological importance. By regulating insect populations [2], the fungus prevents overpopulation that could destabilize ecosystems and overconsume resources.
Interestingly, the significance of Cordyceps extends beyond its macabre life cycle. In Himalayan cultures, some species have been prized for centuries as natural remedies for enhancing vitality and endurance. Today, the fungus is not only a marvel of nature but also a valuable resource in traditional medicine and modern health supplements.
With hundreds of identified species of Cordyceps, at least 35 are recognized for their potential health benefits and medicinal properties. Among these, a few stand out for their unique biology and uses. Let’s take a closer look.
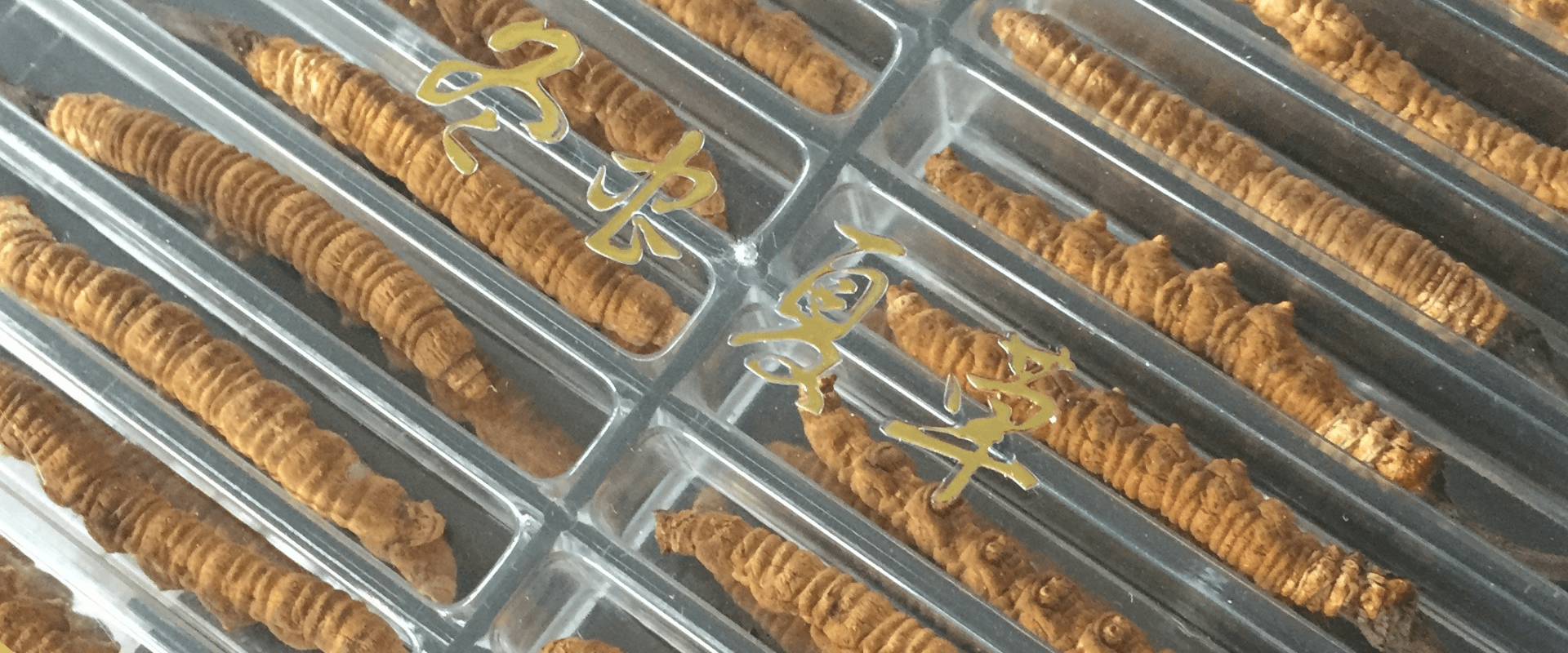
Native to the Tibetan Plateau, this unique fungus has been traditionally used in herbal practices. Known as the 'caterpillar fungus' due to its natural symbiosis with caterpillars, it has been valued for its role in supporting vitality, endurance, and overall well-being.

Unlike Ophiocordyceps sinensis, Cordyceps militaris can be sustainably cultivated without reliance on insect hosts [3]. Its vibrant orange fruiting body is often featured in functional mushroom supplements, offering a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative.

Also known as the “zombie ant fungus,” this species may produce bioactive compounds like red naphthoquinones with potential anti-malarial properties [4]. Famous for its mind-control abilities, it compels the infected ants to climb vegetation for optimal spore dispersal.
Beyond its chilling behavior, this fungus showcases the ecological significance [5] and biotechnological potential [6] of Cordyceps.
The zombie-like behavior Cordyceps triggers in its hosts is a masterstroke of evolutionary adaptation. By releasing targeted enzymes and chemical compounds, the fungus overrides the insect's behavior.
Ophiocordyceps unilateralis fungus infects an ant’s behavior, directing the infected ant to climb a plant stalk and clamp onto it in a “death grip” [7] This ensures the fungus's fruiting body will grow in an advantageous location for fungal spore dispersal.
Over time, the fungus consumes the insect from the inside, using it as a living incubator before completing its reproductive cycle. The methodical precision of this process has fascinated scientists and inspired popular media, from novels like “The Girl With All the Gifts” to the video game (and TV series) “The Last of Us”.
No, Cordyceps cannot control or infect humans or the human body. Its mechanisms for parasitism are strictly species-specific, finely tuned to the biology of its insect hosts over millions of years.
Humans lack the biochemical pathways that the parasitic fungus uses to infiltrate and manipulate insects. So, rest easy—there’s no real-life zombie apocalypse in the making.
This species-specific adaptation is precisely what fascinates scientists. By studying how Cordyceps targets insects so effectively, researchers hope to uncover new insights into parasitism, fungal biology, and potentially even functional applications.

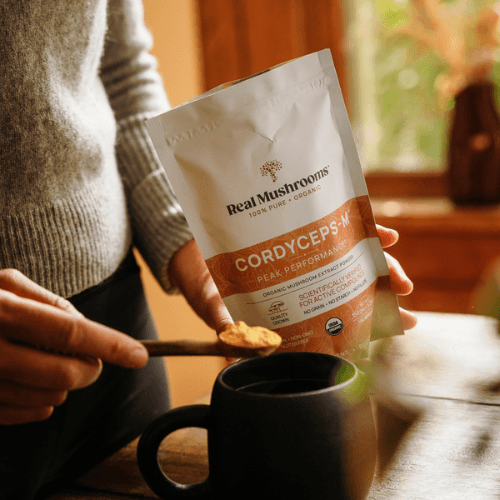
In recent years, Cordyceps has enjoyed a surge in popularity as a key ingredient in health supplements, prized for its potential benefits like supporting health energy levels, overall respiratory health, and supporting immune function. These supplements are commonly derived from other species like Ophiocordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militaris.
Cordyceps is used by some to support energy levels and endurance, particularly among active individuals. This property makes it particularly popular among athletes [8] and those looking to increase respiratory capacity [9]. Cordyceps is used by some to support energy levels and endurance, particularly among active individuals.
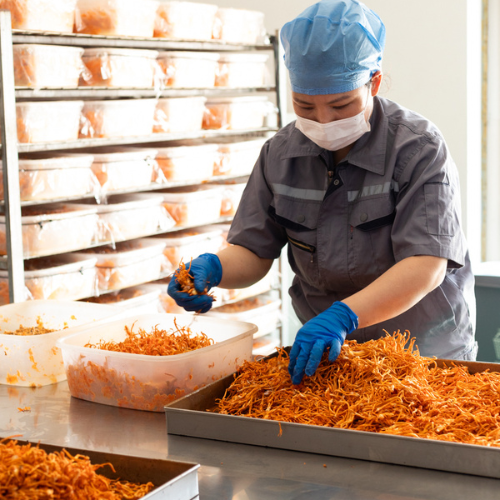
When in doubt, boost your diet with a product that uses scientifically tested production methods that ensure Cordyceps extracts retain maximum potency. These supplements are often derived from the mushroom (fruiting body of the fungus), where most of its bioactive compounds are concentrated, rather than from mycelium grown on grain.
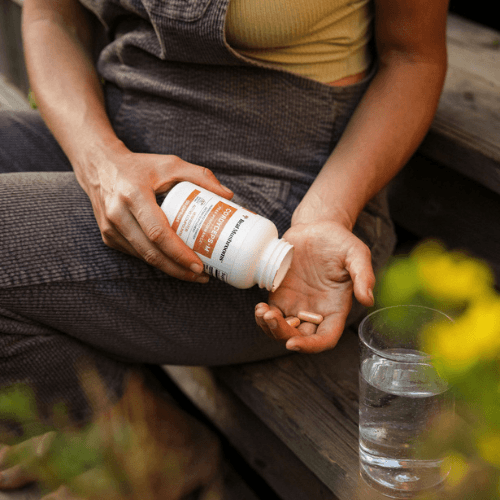

Cordyceps mushrooms are often available as powders, capsules, and tinctures. Some of the most noted benefits include:
When selecting supplements, focus on products that prioritize the use of high-quality ingredients to ensure effectiveness. This means avoiding products that use myceliated biomass, as that is simply the root structure of the mushroom and the grain it is grown on. Such products are low in bioactive compound concentration and high in starch from the grain.
Cordyceps is more than just a parasite that turns other insects into improbable climbers. It is a vital part of its ecosystem, helping regulate populations and maintain biodiversity. For humans, it serves as a bridge between ancient traditions and modern wellness, offering a range of potential health benefits.
By understanding its lifecycle, ecological importance, and functional applications, we can appreciate this strange and spectacular organism on a deeper level.

 .
.Disclaimer: The information or products mentioned in this article are provided as information resources only, and are not to be used or relied on to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. This information does not create any patient-doctor relationship, and should not be used as a substitute for professional diagnosis and treatment. The information is intended for health care professionals only. The statements made in this article have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Any products mentioned are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The information in this article is intended for educational purposes. The information is not intended to replace medical advice offered by licensed medical physicians. Please consult your doctor or health practitioner for any medical advice.