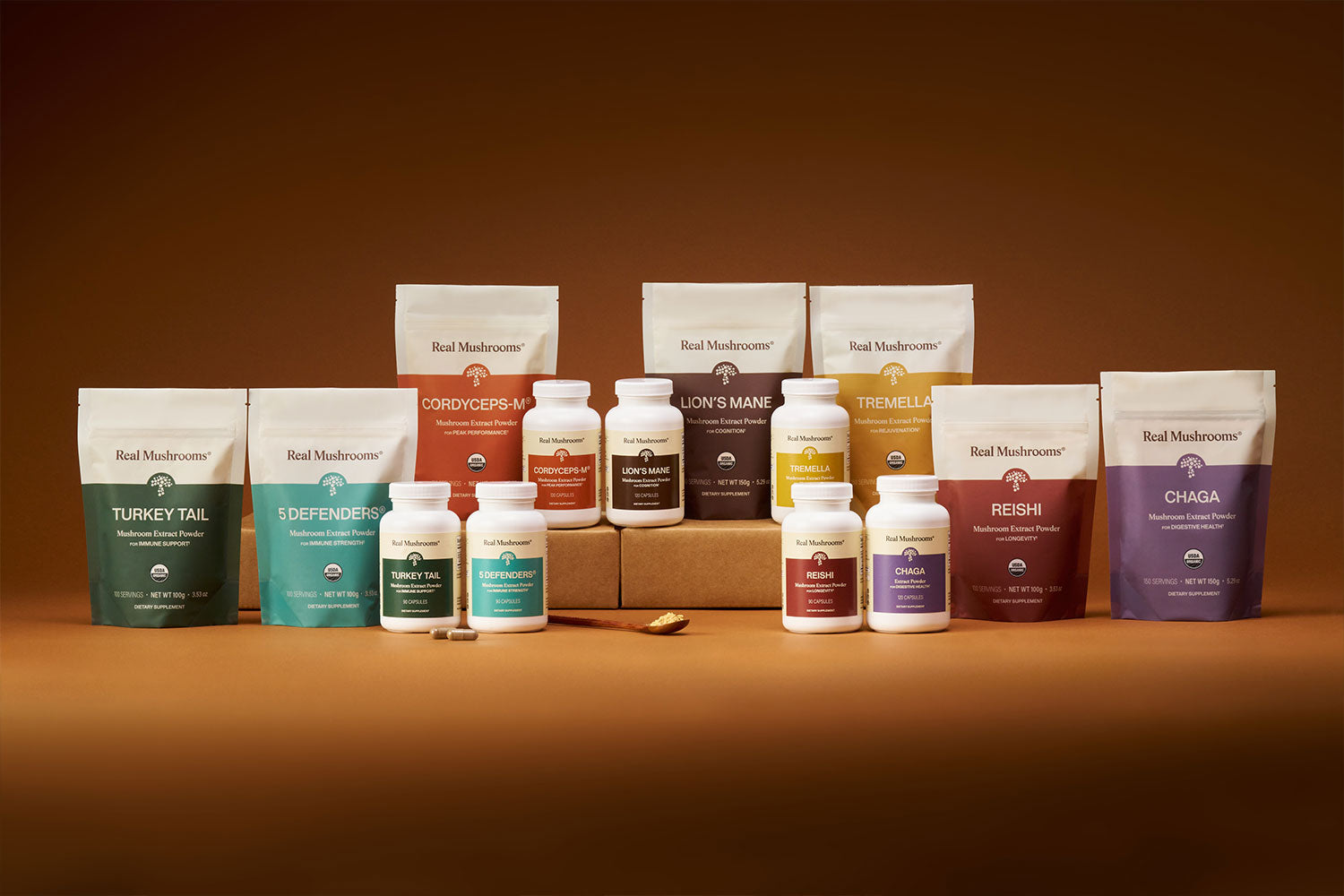
Functional Mushroom Benefits: “Mycelium vs Fruiting Body”
13 minute read
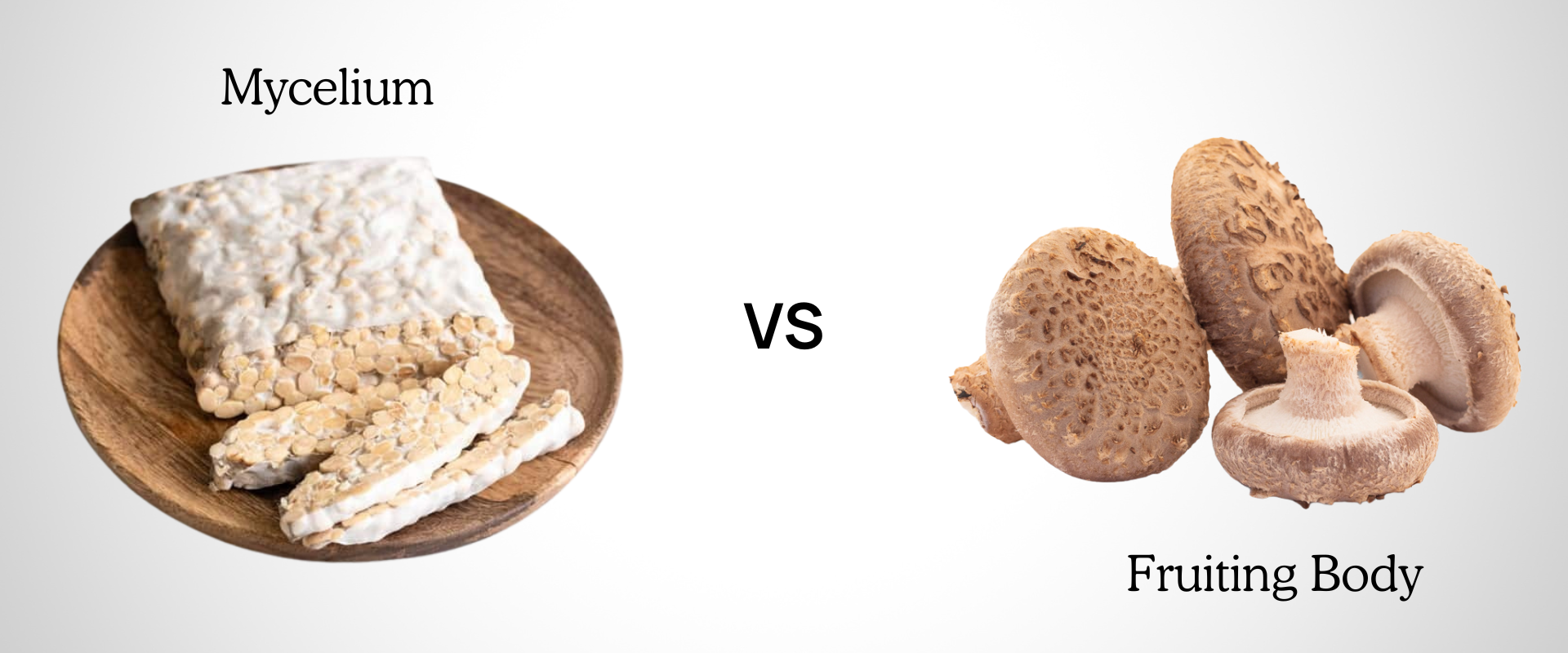

Not all fungal products are equal. Functional "mushroom" products generally contain EITHER the mushroom (fruiting body) OR the mycelium (vegetative body). Notice the quotations around the word "mushroom."
Read on to learn the myths and facts about functional mushroom supplements to get the most functional health support from fungi.
In This Article
- To Benefit from a Functional Mushroom, You Need to Know What You’re Getting
- Fruiting Body, Mycelium, and Marketing Hype
- Fruiting Body vs. Mycelium
- A Closer Look at Mycelium Fermented Grain
- Is That Supplement Made of Real Mushrooms?
- How to Choose an Effective Mushroom Extract
To Benefit from a Functional Mushroom, You Need to Know What You’re Getting
If you want to benefit from the bioactive compounds in these fungi, it’s extremely important to know which part you’re getting when you purchase a supplement. And with so many products on the market making claims about ingredients and efficacy, it can be challenging to understand what will truly support your health.
Listen below to master clinical herbalist Dr. Terry Willard, as he summarizes the issue:

Fruiting Body, Mycelium, and Marketing Hype
The way many supplement brands market and sell their fungal products is cause for concern. If consumers don’t know what to look for when buying a functional mushroom supplement, they may easily be misled by the packaging, naming, and labeling of the vast products available.
Mushroom product labeling requirements from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) tell manufacturers to clearly distinguish whether the product contains actual mushroom (the fruiting body) or just the mycelium in any food or supplement product. But not everyone follows these rules and this is low on the FDA's enforcement priorities.
In 2017, The American Herbal Products Association (AHPA) released labeling guidance for Fungi Dietary Ingredients. This is not enforceable but gives recommendations on how fungal products should be accurately labeled to clearly inform the consumer on what is in the product.
Too often, brands disguise the true nature of their products and misdirect consumers who want to buy effective functional mushroom products. Here, we will separate the myths from the facts about mushroom terminology, their active compounds, and the marketing hype to give you the information you need to buy a supplement with the most functional mushroom benefits.
Comparing Mushrooms and Mycelium: Whole mushroom extracts contain all the nutrients and bioactive compounds with substantial health benefits in humans. This is why mushroom supplements are more active than mycelium fermented grain products.
Fruiting Body vs. Mycelium
It is important to reiterate that just as a mushroom is not mycelium, mycelium is also not a mushroom. These terms are not synonymous and should be accurately differentiated.
To reap the health benefits of functional mushrooms, you need a supplement with high concentrations of the parts of the fungi that offer the most therapeutic compounds. So you can truly experience the adaptive health benefits of functional mushroom supplementation, this section discusses the difference between "mycelium vs fruiting body" extracts so you can make informed purchasing decisions.
The Difference Between Fungal Parts
The spores are in the surrounding air all around us, and under favorable conditions, these will germinate and begin to grow branching filaments called hyphae. As the hyphae continue to grow, they will fuse together to form fungal mycelium.
Fungal mycelium is an underground network that expands and feeds off of organic plant matter. This phase of the basidiomycetes’ life cycle is the vegetative stage or the vegetative body of the organism.
During this time, the fungal mycelium produces enzymes that break down the plant material in its growth radius and recycle it into beneficial compounds that return to the soil. In nature, this typically means that fungal mycelium will form large networks of fungal matter by breaking down wood, logs, leaves, and other plant matter.
The plant matter on which fungi feed is commonly referred to as the substrate. The fungal mycelium becomes entwined in whatever substrate, making an inseparable mass of substrate and mycelium.
If environmental conditions are right, the mycelium will produce a mushroom, a.k.a. the fruiting body. The mushroom is actually the reproductive structure of this organism. When fully mature, it produces spores that, when distributed across plant matter, will allow for the creation of new mycelial networks and the spread of the fungus.
Mycelial networks can live for hundreds if not thousands of years and spread across vast distances. <2> In fact, the largest organism on earth is a mycelial mat of a honey mushroom in eastern Oregon that is 890 hectares in size and over 2,000 years old!
Fungal Life Cycle

Identifying Fillers in Your Supplement
Read the mushroom or mycelium supplement package ingredients to see which part of these fungi the producer used. Based on the labeling, the product could be any combination of the following:
- Mycelium
- Mushroom
- Sclerotium
- Spore
- Substrate matter
These materials are dried, ground into a powder and then potentially extracted.
The majority of commercial producers grow mycelium on grains like rice, oats, or sorghum. Therefore, all that grain becomes inseparable from the mycelium and remains in the final product, leading to high amounts of starch.
When mycelium fermented grain forms the bulk of a supplement, the grain acts as a filler and "dilutes" the product because it doesn’t contain any bioactive compounds. Mycelium fermented grain dramatically reduces how much beneficial compounds are in each serving of your supplement.

The Key Functional Compound in Mushrooms: Beta-Glucans
Functional mushroom benefits are derived from their active compounds, which are found in abundance in the mushroom (fruiting body) itself and less so in the mycelium. The most important of the key bioactive compounds in fungi are called beta-glucans, and they offer a host of health benefits. <4>
Current research shows that beta-glucans’ most important benefit to our health is to modulate the immune system. Additionally, they can help regulate blood sugar, improve feelings of fatigue, and increase overall endurance.<5>
In some cases, beta-glucans can have a positive effect on malignant conditions based on their ability to increase certain immune cells that increase autophagy.* <6>
Also, consider that functional mushrooms have been used as herbal medicine for thousands of years in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), with varieties like reishi, shiitake, maitake, lion’s mane, turkey tail, and cordyceps being the most revered for their powerful health benefits. TCM practitioners still use functional mushrooms to treat a host of different ailments and health conditions. <7>
Nowadays, the health benefits of functional mushrooms can be sourced from mushroom supplements, whether in powder, capsule, or tincture form. This allows people to easily enjoy the nutritional advantages for human consumption, which include support for natural immune systems.
Beta-Glucans: "Mycelium vs Fruiting Body"
The chart below shows the significant difference between mushrooms (fruiting bodies), pure mycelium and mycelium fermented grain Pure mycelium can be produced by growing the mycelium in a liquid substrate instead of a solid substrate.
This is known as liquid fermentation.
At the end of the growing process involved in direct human food cultivation, the liquid can be drained off, yielding pure mycelium. However, most producers of mycelial products grow the mycelium on a grain substrate.
The Percentage of Beta-glucans and Alpha-glucans in Cordyceps Mushrooms and Cordyceps Mycelium
| Beta-glucans | Alpha-glucans | |
| Cordyceps militaris mushroom | 34.36% | 1.65% |
| Cordyceps Cs-4 (Pure mycelium) | 7.58% | 1.61% |
| Cordyceps mycelium grown on grain | 1.5% | 64% |
Analytical data courtesy of Nammex™
The consistency of Alpha-glucans content between mushrooms (fruiting bodies) and pure mycelium confirms that the extremely high alpha-glucans in mycelium fermented grain are from the undigested grain in the final product.
A helpful example of visualizing mycelium fermented grain is the food product tempeh. Tempeh is a traditional cake-like Indonesian food that is made from cooked soybeans fermented with a fungus.

The producer packs the tempeh and forms it into patties or logs.
As the fungus grows on the soybeans, it becomes an inseparable mass, which they sell as a meat replacement food. Similarly, with mycelium fermented grain, the resulting finished product retains BOTH the mycelium and the grain substrate it grows on.
Mycelium Vs Mushrooms (Fruiting Bodies): Generally, essential amino acids are present in both mycelium and mushrooms (fruiting bodies). However, the amount of amino acids may vary based on the extraction method and type of function mushroom grown.
A Closer Look at Mycelium Fermented Grain
With that tempeh visual clearly in mind, let’s now take a closer look at the makeup of a mycelium fermented grain product. Let's calculate the percentage of mycelium in the finished product. This will help to put the analytical data presented above into context.
Brown rice is a common substrate, so let’s use that as an example. Imagine 1 kg of cooked brown rice is inoculated with turkey tail mycelium and allowed to ‘ferment’.
The conversion of brown rice to mycelium is never 100% complete, and patents held by mycelium fermented grain producers claim approximately 35% conversion. Therefore, on completion, the fermented foods will result in approximately 650 g of brown rice remaining and 350 g converted into mycelium.
Because the moisture content of cooked brown rice and mycelium is different, a calculation must be made to arrive at the dry weights. Brown rice contains about 50% moisture, and mycelium is 90% moisture.
Therefore, after drying, the mycelium fermented grain contains 325 g of dry brown rice and only 35 g of dry mycelium. As a percentage, dry mycelium is just 9.7% of the total weight.
So, two capsules or 1,000 mg of mycelium fermented grain, which is the standard serving size, contain only 97 mg of dry mycelium. Or stated another way, 20 capsules are required to equal 1,000 mg of mycelium.
Furthermore, mycelium, like mushrooms (fruiting bodies), needs to be extracted (most commonly with hot water) to access the beta-glucans and other functionally relevant molecules, such as ergothioneine, ergosterol, and secondary metabolites.
In contrast, mycelium fermented grain products are not typically extracted.
On the other hand, you would need only 2 capsules of our Turkey Tail Extract supplement to get 1000 mg of extracted whole mushroom powder.
So, whichever way you look at it, not all fungal products are equal!
If mycelium fermented grain offers any health benefits, they likely arise from the ‘fermented’ grain, such as short-chain fatty acids or perhaps other as-yet unidentified unique post-biotic molecules.
Is That Supplement Made of Real Mushrooms?
Too often, manufacturers of products using mushroom extracts bring functional mushroom products to market with claims of being pure mushroom extracts. However, the product could be any combination of mushrooms (fruiting bodies), mycelium, sclerotium, spore, and substrate matter.
There are many documented cases of mushroom supplement packaging and labeling that obscures or outright misrepresents what the buyer is getting exactly. This marketing misstep causes consumers a lot of confusion and jeopardizes the integrity of the supplement market.

Investigating Mushroom Supplement Integrity: Reishi (Ganoderma lucidum) Products
Part of the issue facing the mushroom industry is the lack of standardized testing for various mushroom types. However, reishi mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum) is an exception.
Given its long-standing use in traditional Chinese medicine, researchers have developed reliable testing methods for identifying reishi bioactive compounds in products.
Using these proven testing methods, six scientific researchers conducted and published a study in partnership with the US Pharmacopoeia to evaluate 19 reishi mushroom supplements purchased online in the U.S.A. from websites such as Amazon and eBay. Only FIVE of the 19 supplements (26.3%) contained genuine reishi.
The sample of products evaluated in the study included six mushroom supplements, one mushroom powder with added polysaccharides, one reishi mycelia product and eleven extracts. The results of this reishi supplement study indicate that several commercially available mushroom supplements do not contain what the consumer expects based on product information and labels.
Additionally, ConsumerLab investigated reishi supplements and uncovered contradictions between product labeling and product contents of mushroom supplements. One of the seven top-selling brands they analyzed made claims on its label that could not be supported.
The brand’s product name includes the term “mushroom” and the packaging features an image of mushrooms (fruiting bodies) on the front. However, the product itself contained reishi mycelium only and no mushrooms whatsoever.
ConsumerLabs went on to say that, “Its chemical fingerprint matched that of mycelium, but the inclusion of “mushroom” in the product’s name and the image of fruiting body, rather than mycelium, on the front label could lead a person to believe that the product contains reishi mushroom and to expect concentrations of compounds normally found in the fruiting body. In fact,
Fungi Buyer Beware: What to Look Out For
The above examples illustrate an ongoing problem within the functional mushroom industry as well as mushroom supplements in general. Consumers need to be aware of what they’re getting to ensure they purchase only genuine mushroom powders, pills, and tinctures from reliable suppliers.
Real Mushrooms only uses extracts from the mushroom (fruiting body) itself and doesn’t include any substrate matter or fillers in its formulation. We label our products to show exactly what ingredients we include and from what part of the fungi. Further, we list the percentage of Beta-Glucans in each serving.
By carefully reading the ingredients on any supplement label, selecting a product with the mushroom (fruiting body) as the primary content, and choosing organic suppliers who list the percentage of functional compounds (Beta-Glucans) in each serving, you can improve your chances of buying a high-quality mushroom extract powder with effective functional concentrations.
Therefore, to get the most potent and high-value functional fungi supplement, look for extracts made from the mushroom (fruiting body) that also specify beta-glucan content. Also, refrain from buying supplements that do not specifically state the part of the fungi they use, these may be mycelial products that have lesser nutritional value.
The ingredients label should say whether you are getting the mushroom, the mycelium, or a blend of both.
Containing no mycelium fermented grain and other fillers, Real Mushrooms supplements deliver a high-potency dosage of functional beta-glucans per serving, the main active compound in mushrooms and mycelium. We list the beta-glucans content of all our products to show and guarantee you that they are present.

Different Functional Mushroom Varieties: Not all mushroom supplements have the same effects. For example, some mushrooms have greater impact in gut health while others are more effective in supporting natural immune function.
How to Choose an Effective Mushroom Extract
A Mushroom Supplement Buying Guide
By understanding the difference between mushrooms and mycelium, you can cut through the noise and make an informed product choice. To know what you are getting and reap full benefits from these fungal wonders, shop with these guidelines in mind:
- Read the product's Supplement Facts panel and attempt to distinguish the true contents of the product.
- Select products that primarily contain the mushroom (fruiting body), not just mycelium, myceliated grain, or myceliated biomass.
- Avoid buying products that lack specific information about the plant part of the fungi (whether mushroom or mycelium).
- Look for an extract as extraction breaks down the fungal cell wall and improves bioavailability.
- Look for brands that list the beta-glucans content in their Supplement Facts panel. It's important for it to be in the Supplement Facts panel and not just in any marketing materials.
- Ignore any polysaccharide numbers because polysaccharides also measure starches.
- Make sure the ingredients are organically grown.
- Always choose to buy from a trusted source. Ideally, the source will have been validated by third-party labs.
Related Articles
- How Mushrooms Support Ecosystem Health and Biodiversity
- Edible Wild Mushrooms: 2 Categories & Their Benefits
- Do Mushrooms Have Protein? 4 Findings and Other Nutrition Facts
- How Are Mushrooms Good for Dogs & Cats?
References
- 24.3D: Basidiomycota- The Club Fungi (2018) Biology LibreTexts. Available at: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/General_Biology_(Boundless)/24%3A_Fungi/24.03%3A_Classifications_of_Fungi/24.3D%3A_Basidiomycota-_The_Club_Fungi.
- Ecologist's Notebook. (2024). Available at: https://sites.psu.edu/ecologistsnotebook/page/4/ (Accessed: 22 August 2024).
- Berger, R.G. et al. (2022) ‘Mycelium vs. Fruiting Bodies of Edible Fungi—A Comparison of Metabolites’, Microorganisms, 10(7), p. 1379. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071379.
- Mirończuk-Chodakowska, I., Kujawowicz, K. and Witkowska, A.M. (2021) ‘Beta-Glucans from Fungi: Biological and Health-Promoting Potential in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era’, Nutrients, 13(11), p. 3960. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113960.
- Geng, P. et al. (2017) ‘Antifatigue Functions and Mechanisms of Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms’, BioMed Research International, 2017. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9648496.
- Wang, M., Pan, J., Xiang, W., You, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., & Zhang, A. (2024). β-glucan: a potent adjuvant in immunotherapy for digestive tract tumors. Frontiers in Immunology, 10, Article 1424261. Available at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1424261/full (Accessed: 22 August 2024).
- Łysakowska, P., Sobota, A. and Wirkijowska, A. (2023) ‘Medicinal Mushrooms: Their Bioactive Components, Nutritional Value and Application in Functional Food Production—A Review’, Molecules, 28(14), pp. 5393–5393. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145393.