Menu
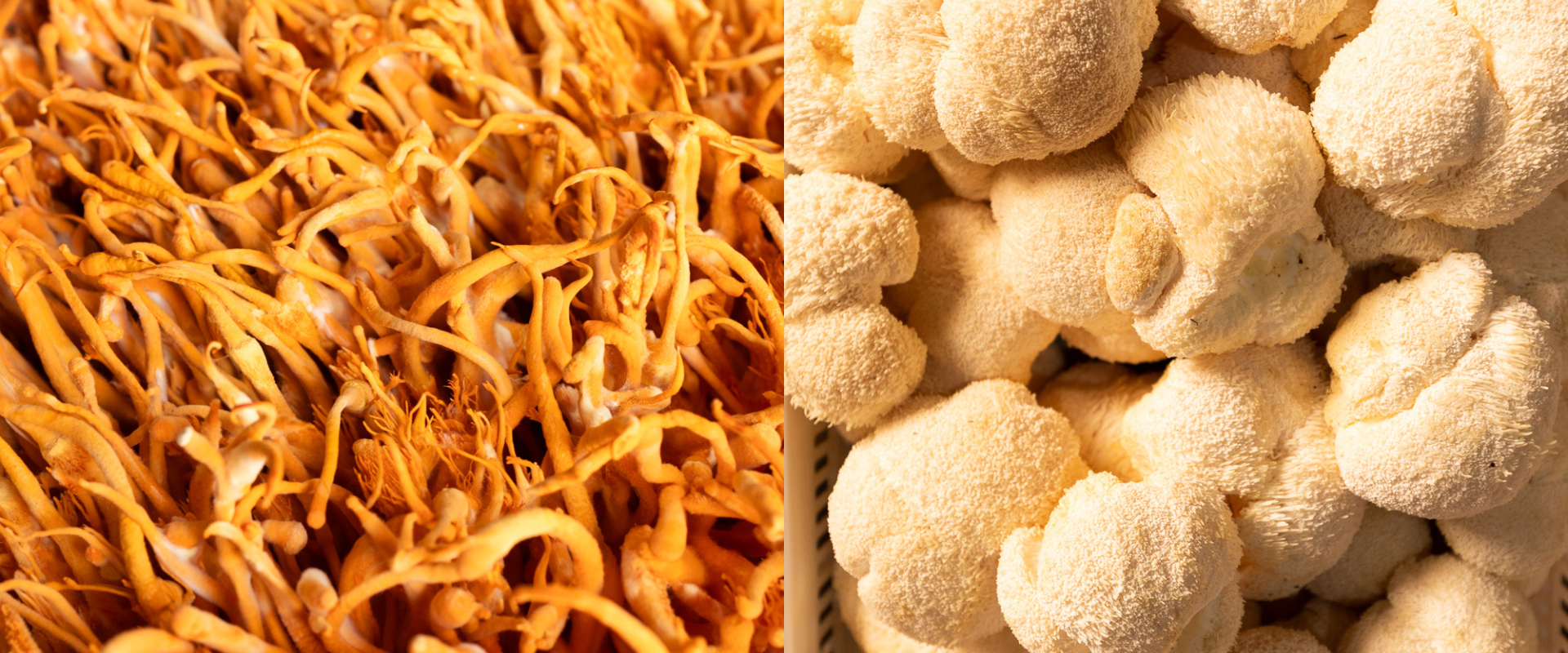


Mushrooms have been valued for centuries in traditional medicine and as functional foods because of their potential health benefits, and two of the most popular varieties today are Cordyceps and Lion’s Mane. These functional mushrooms have distinct properties, potential wellness benefits, and unique compounds that make them stand out.
While cordyceps mushrooms are often associated with energy, endurance, and respiratory health, the lion’s mane mushroom is linked to cognitive support and nervous system health. This article provides a detailed comparison of these two remarkable fungi, their traditional uses, research-backed properties, and how they can be incorporated into wellness routines for maximum health benefits.

Cordyceps is a genus of parasitic fungi that grows on insect larvae, particularly in high-altitude regions such as the Himalayas. The two primary species used in supplements are Cordyceps sinensis (Ophiocordyceps sinensis) and Cordyceps militaris. The former was traditionally harvested in the wild and is now difficult to source due to conservation concerns. The latter is more commonly cultivated and studied due to its high concentration of active compounds, particularly cordycepin. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Cordyceps has long been used to support stamina, energy levels, and lung function.
Lion’s Mane (Hericium erinaceus) is a white, shaggy mushroom that resembles a lion’s mane as it grows. It is found on hardwood trees in North America, Europe, and Asia. Unlike Cordyceps, Lion’s Mane is not parasitic but rather a saprophytic fungus, meaning it grows on decaying wood. This mushroom has been widely studied for its potential to support brain health, memory, mood, and nervous system regeneration. It has been used in traditional medicine in China and Japan for centuries as a tonic for the brain and gut, among other health benefits.
Cordyceps contains several bioactive compounds that contribute to its health benefits. Among these, cordycepin is a unique nucleoside that has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory and energy-supporting properties. Adenosine, another compound, plays a role in ATP (energy) production in the body, potentially explaining Cordyceps’ historical use for vitality and endurance. Additionally, Cordyceps contains polysaccharides, which may contribute to immune modulation and antioxidant activity.
On the other hand, the Lion’s Mane mushroom is rich in compounds known as hericenones and erinacines, which may support nerve growth factor (NGF) synthesis. Hericenones are found in the fruiting body and are believed to support cognitive function, while erinacines are found in the mycelium and studied for their potential neuroprotective effects. Like Cordyceps, the Lion’s Mane mushroom also contains polysaccharides and beta-glucans, which may support immune health and antioxidant activity.
Cordyceps may support ATP production, the body’s main energy currency, making it a favorite among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Research has explored its role in supporting endurance and oxygen utilization in the body. Beyond performance, Cordyceps has been traditionally used in TCM to support overall vitality, including respiratory function. Additionally, Cordyceps may support energy levels and endurance, as some research suggests it may support post-exercise recovery and energy levels.
Lion’s Mane is often associated with cognitive support and maintaining a healthy nervous system. It may play a role in supporting cognitive health. The presence of erinacines and hericenones suggests they may support nerve function and overall neurological health. Additionally, the Lion’s Mane mushroom may provide mood support, with a possible role in emotional well-being and stress resilience. Lion’s Mane may also act as a potential tool for supporting healthy sleep quality, making it an interesting option for those struggling with occasional sleep disturbances.

The cordyceps mushroom has a long history of use in Traditional Chinese Medicine, where it has been used as a tonic for vitality, kidney health, and respiratory support. Modern applications include its use in healthy pre-workout supplements, energy tonics, and respiratory health formulas. The cultivation of Cordyceps militaris has made it more widely accessible, and it is now commonly included in various wellness products.
The Lion’s Mane mushroom has been used in East Asian food and medicine for digestive health, immune system support, skin health, and brain function. Today, it is a popular ingredient in supplements that support cognitive function, functional beverages, and powdered extracts for brain health support. Unlike Cordyceps, Lion’s Mane is also enjoyed in culinary applications, as it has a mild, seafood-like flavor and a meaty texture that works well in vegetarian food.

Both Cordyceps and Lion’s Mane are available in various forms, including capsules, powders, tinctures, and even whole mushrooms in the case of Lion’s Mane. Capsules are a convenient way to ensure consistent dosing, while powders can be mixed into smoothies, coffee, or tea. Tinctures, which are alcohol or water extracts, may provide faster absorption.
Cordyceps is often taken in the morning or before exercise to support healthy energy levels. Lion’s Mane, depending on individual preference, may be taken in the morning for focus or in the evening for potential relaxation benefits. Some users find that taking Lion’s Mane before bed supports deep sleep, thanks to its possible influence on the nervous system.

Both Cordyceps and Lion’s Mane are generally considered safe for most people when consumed in appropriate amounts. However, Cordyceps may interact with medications affecting immune function and blood clotting. Lion’s Mane may cause mild digestive discomfort in some individuals. Additionally, it may help slightly lower blood sugar levels, which could be a consideration for those with diabetes or blood sugar concerns. As always, those with mushroom allergies or taking prescription medications should consult a healthcare provider before using these supplements.

While both mushrooms offer unique benefits, their primary applications are distinct. Cordyceps is most often used for energy, stamina, and physical endurance, while Lion’s Mane is known for its cognitive function and nervous system support. For those looking to optimize physical performance, Cordyceps may be the better option, whereas individuals seeking enhanced memory, focus, and mood support may find the Lion’s Mane mushroom more beneficial. Understanding their differences allows for better integration into individual wellness routines.
Cordyceps and Lion’s Mane mushrooms each offer unique potential benefits and applications. If you’re looking to support energy, endurance, and physical performance, Cordyceps might be the better choice. If cognitive function and nervous system health are your focus, then Lion’s Mane could be more suitable.
As with all dietary supplements, it’s best to choose high-quality mushroom supplements from reputable sources and consult a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your wellness routine.

 .
.Disclaimer: The information or products mentioned in this article are provided as information resources only, and are not to be used or relied on to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. This information does not create any patient-doctor relationship, and should not be used as a substitute for professional diagnosis and treatment. The information is intended for health care professionals only. The statements made in this article have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Any products mentioned are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The information in this article is intended for educational purposes. The information is not intended to replace medical advice offered by licensed medical physicians. Please consult your doctor or health practitioner for any medical advice.