Menu

In the world of holistic medicine, the potential of natural substances often outshines synthetic alternatives. One such naturally occurring compound that has recently garnered attention is ergothioneine. Found abundantly in mushrooms, ergothioneine is proving to be a key player in supporting cognitive function and overall brain health.
Watch the video below or read on as I delve into the remarkable benefits of ergothioneine, particularly for practitioners, holistic medicine enthusiasts, and those exploring the health benefits of mushrooms.
Ergothioneine is a unique amino acid derivative, primarily sourced from mushrooms. Its discovery dates back to the early 20th century, and since then, it has been recognized as a powerful antioxidant and cytoprotective agent. Unlike other antioxidants, ergothioneine has a special role in protecting cells from oxidative stress, a major contributor to cognitive decline and various neurodegenerative diseases.
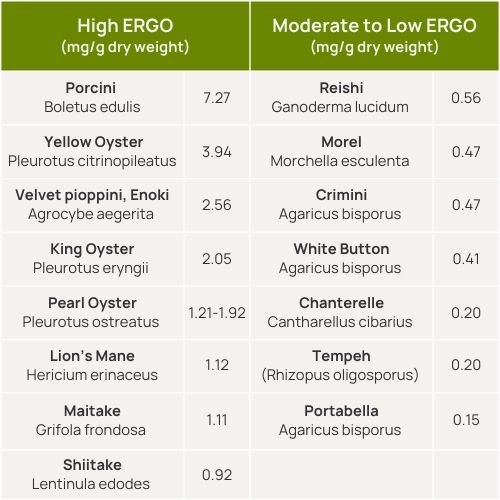
When we think about cognitive health and mushrooms, Lion’s Mane is often the first mushroom that comes to mind. However, research shows that regular consumption of any edible mushroom can yield significant cognitive benefits. Ergothioneine is the secret behind this, as it is found in varying concentrations across different mushroom species.
The human body cannot produce ergothioneine, yet we have dedicated transporters in our cells to absorb and retain it. This highlights its evolutionary importance. Ergothioneine’s ability to switch between active and inactive forms depending on the cell’s pH level makes it an adaptive antioxidant, crucial for maintaining cellular health, particularly in the brain.
As a practitioner or holistic health enthusiast, understanding the role of ergothioneine can enhance your approach to cognitive health. For clients or personal use, consider recommending a diet rich in mushrooms or high-quality mushroom supplements to leverage the cognitive benefits of ergothioneine.

Beyond its cognitive benefits, ergothioneine is linked to broader health outcomes:
Incorporating ergothioneine into daily health regimens—whether through diet or supplementation—is a practical and effective way to enhance cognitive function and protect against neurodegenerative diseases. For those committed to holistic health, ergothioneine offers a natural, multi-benefit option to support long-term cognitive health and overall wellness.
Start including mushrooms in your diet today and consider ergothioneine supplements as part of a comprehensive approach to maintaining cognitive health. As always, consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best regimen for your individual needs.

Disclaimer: The information or products mentioned in this article are provided as information resources only, and are not to be used or relied on to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. This information does not create any patient-doctor relationship, and should not be used as a substitute for professional diagnosis and treatment. The information is intended for health care professionals only. The statements made in this article have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Any products mentioned are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The information in this article is intended for educational purposes. The information is not intended to replace medical advice offered by licensed medical physicians. Please consult your doctor or health practitioner for any medical advice.